Abstract Interface
This chapter documents the abstract interface to access a result data structure.
| Functions | Description |
|---|---|
SignalType | Predefined enumeration defining the supported signal types. |
rawSignal | Return raw signal data given the signal name (required). |
signalNames | Return all signal names (required). |
timeSignalName | Return the name of the time signal (required). |
hasOneTimeSignal | Return true if one time signal present (required). |
getSignalDetails | Return details of signal data (optional). |
hasSignal | Return true if signal name is known (optional). |
defaultHeading | Return default heading as string (optional). |
Predefined enumeration
ModiaResult.SignalType — Type@enum ModiaResult.SignalTypeDefines the type of the signal. Supported values:
ModiaResult.Independent: Independent variable (usually the time signal).ModiaResult.Continuous: Piece-wise continuous signal (typically linearly interpolated).ModiaResult.Clocked: Clocked signal (values are only defined at the correspondingTimesignal time instants and have no value in between; the latter might be signaled by piece-wise constant dotted lines).
Required functions
The following functions must be defined for a new result data structure.
ModiaResult.rawSignal — Function(timeSignal, signal, signalType) = ModiaResult.rawSignal(result, name)Given the result data structure result and a variable name::AbstractString, return the result values of the independent variable (= timeSignal), the corresponding result values of the variable (= signal) and the type of the signal signalType::SignalType). Note, an error shall be raised, if name is not known.
The following figure sketches the returned timeSignal and signal data structures:
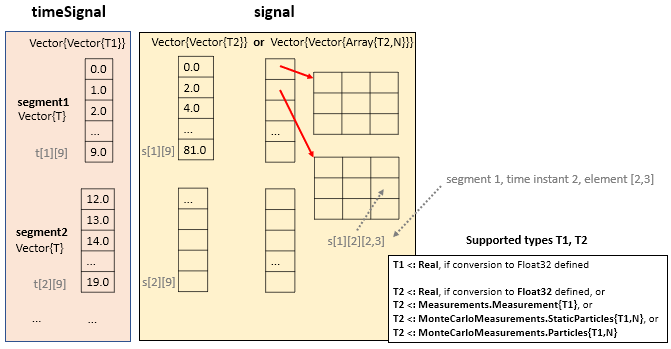
Other signal types might be mapped to this basic signal type by introducing views.
Details of the return arguments
timeSignal::Vector{Vector{T1}}: A result consists of one or more segments. timeSignal[i][j] is the value of time instant j in segment i. timeSignal[i][:] must have monotonically increasing values and type T1<:Real must be a subtype of Real for which a conversion to AbstractFloat is defined. For example, T1::Rational is fine, but T1::Complex is not allowed.
signal::Vector{Vector{T2}} or signal::Vector{Vector{Array{T2,N}}}: signal[i][j] is the value of the variable at time instant timeSignal[i][j]. This value can be a scalar or an array. Type T2 can have one of the following values:
T2 <: Real, must be a subtype ofRealfor which a conversion toAbstractFloatis defined, orT2 <: Measurements.Measurement{T1}, orT2 <: MonteCarloMeasurements.StaticParticles{T1,N}, orT2 <: MonteCarloMeasurements.Particles{T1,N}.
If the signal is a constant with value value, return ([[t_min, t_max]], [[value, value]], ModiaResult.Continuous).
If the signal is the time signal, return (timeSignal, timeSignal, ModiaResult.independent). The timeSignal might be a dummy vector consisting of the first and last time point in the result (if different timeSignals are present for different signals or if the signal is constant).
signal and timeSignal may have units from package Unitful.
The information signalType::SignalType defines how the signal can be interpolated and/or plotted.
ModiaResult.signalNames — FunctionModiaResult.signalNames(result)Return a string vector of the signal names that are present in result.
ModiaResult.timeSignalName — FunctionModiaResult.timeSignalName(result)Return the name of the independent variable (typically: "time").
ModiaResult.hasOneTimeSignal — FunctionModiaResult.hasOneTimeSignal(result)Return true if result has one time signal. Return false, if result has two or more time signals.
Optional functions
The following functions can be defined for a new result data structure. If they are not defined, a default implementation is used.
ModiaResult.getSignalDetails — Function(signal, timeSignal, timeSignalName, signalType, arrayName,
arrayIndices, nScalarSignals) = getSignalDetails(result, name)Return the signal defined by name::AbstractString as signal::Vector{Matrix{<:Real}}. name may include an array range, such as "a.b.c[2:3,5]". In this case arrayName is the name without the array indices, such as "a.b.c", arrayIndices is a tuple with the array indices, such as (2:3, 5) and nScalarSignals is the number of scalar signals, such as 3 if arrayIndices = (2:3, 5). Otherwise arrayName = name, arrayIndices=(), nScalarSignals=1.
In case the signal is not known or name cannot be interpreted, (nothing, nothing, nothing, nothing, name, (), 0) is returned.
It is required that the value of the signal at a time instant has either typeof(value) <: Real or typeof(value) = AbstractArray{Real, N}. The following Real types are currently supported:
convert(Float64, eltype(value)is supported (for example Float32, Float64, DoubleFloat, Rational, Int32, Int64, Bool).
Measurements.Measurement{<Type of (1)>}.
MonteCarloMeasurements.StaticParticles{<Type of (1)>}.
MonteCarloMeasurements.Particles{<Type of (1)>}.
ModiaResult.hasSignal — FunctionModiaResult.hasSignal(result, name)Returns true if signal name::AbstractString is available in result.
ModiaResult.defaultHeading — FunctionModiaResult.defaultHeading(result)Return default heading of result as a string (can be used as default heading for a plot).