SignalTables Documentation
Overview
Package SignalTables provides abstract and concrete types and functions for signal tables. A signal table is basically a table where the table columns can be multi-dimensional arrays with attributes. Typically, simulation results, reference signals, table-based input signals, measurement data, look-up tables can be represented by a signal table.
A signal table is an ordered dictionary of signals with string keys. A signal can be defined in the following forms:
- As Var dictionary that has a required values key (or an alias key) representing a signal array of any element type as function of the independent signal(s), or is the k-th independent signal. A signal array is a multi-dimensional array with indices
[i1,i2,...,j1,j2,...]to hold variable elements[j1,j2,...]at the[i1,i2,...]independent signal(s). If an element of a signal array is not defined, it has a value of missing. - As Par dictionary that has a required value key (or and alias key) representing a constant of any type.
- As Map dictionary that has no required keys and collects attributes/meta-data that are associated with a Var, Par, Map, or signal table dictionary.
In all these dictionaries, additional attributes can be stored, for example unit, info, variability (continuous, clocked, ...), interpolation, extrapolation, and user-defined attributes.
Examples
using SignalTables
t = 0.0:0.1:0.5
sigTable = SignalTable(
"time" => Var(values= t, unit="s", independent=true),
"load.r" => Var(values= [sin.(t) cos.(t) sin.(t)], unit="m"),
"motor.angle" => Var(values= sin.(t), unit="rad", state=true, der="motor.w"),
"motor.w" => Var(values= cos.(t), unit="rad/s"),
"motor.w_ref" => Var(values= 0.9*[sin.(t) cos.(t)], unit = ["rad", "1/s"],
info="Reference angle and speed"),
"wm" => Var(alias = "motor.w"),
"ref.clock" => Var(values= [true, missing, missing, true, missing, missing],
variability="clock"),
"motor.w_c" => Var(values= [0.8, missing, missing, 1.5, missing, missing],
variability="clocked", clock="ref.clock"),
"motor.inertia"=> Par(value = 0.02f0, unit="kg*m/s^2"),
"motor.data" => Par(value = "resources/motorMap.json"),
"attributes" => Map(experiment=Map(stoptime=0.5, interval=0.01))
)
phi_m_sig = getSignal( sigTable, "motor.angle") # = Var(values=..., unit=..., ...)
phi_m = getValuesWithUnit(sigTable, "motor.angle") # = [0.0, 0.0998, 0.1986, ...]u"rad"
w_c = getValues( sigTable, "motor.w_c" ) # = [0.8, missing, missing, 1.5, ...]
inertia = getValueWithUnit( sigTable, "motor.inertia") # = 0.02u"kg*m/s^2"
getValues(sigTable, "motor.w") === getValues(sigTable, "wm")
showInfo(sigTable)Command showInfo generates the following output:
name unit size eltypeOrType kind attributes
───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
time "s" [6] Float64 Var independent=true
load.r "m" [6,3] Float64 Var
motor.angle "rad" [6] Float64 Var state=true, der="motor.w"
motor.w "rad/s" [6] Float64 Var
motor.w_ref ["rad", "1/s"] [6,2] Float64 Var info="Reference angle and speed"
wm "rad/s" [6] Float64 Var alias="motor.w"
ref.clock [6] Union{Missing,Bool} Var variability="clock"
motor.w_c [6] Union{Missing,Float64} Var variability="clocked", clock="ref.clock"
motor.inertia "kg*m/s^2" Float32 Par
motor.data String Par
attributes Map experiment=Map(stoptime=0.5, interval=0.01)The various Julia FileIO functions can be directly used to save a signal table in various formats, e.g. JSON or HDF5 (see FileIO Examples, json file of sigTable above ).
The commands
using SignalTables
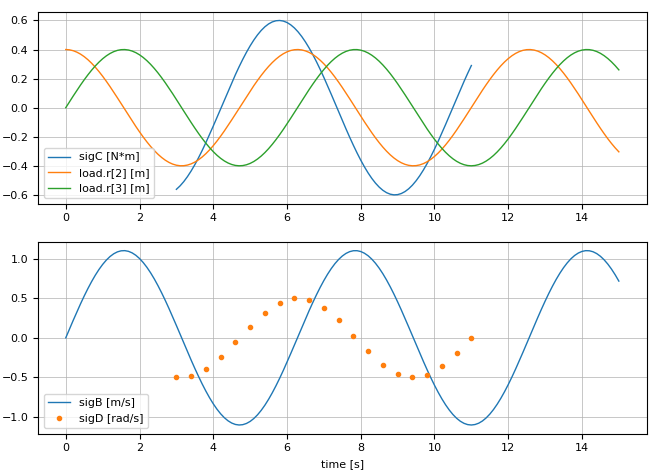
usePlotPackage("PyPlot") # or ENV["SignalTablesPlotPackage"] = "PyPlot"
sigTable = getSignalTableExample("MissingValues")
@usingPlotPackage # = using SignalTablesInterface_PyPlot
plot(sigTable, [("sigC", "load.r[2:3]"), ("sigB", "sigD")])generate the following plot:
Abstract Interfaces
Concrete implementations of the Abstract Signal Table Interface are provided for:
SignalTable(included in SignalTables.jl).Modia.jl (a modeling and simulation environment; version >= 0.9.0)
DataFrames.jl (tabular data; first column is independent variable; only scalar variables))
Tables.jl (abstract tables, e.g. CSV tables; first column is independent variable; only scalar variables).
Concrete implementations of the Abstract Plot Interface are provided for:
PyPlot (plots with Matplotlib from Python; via SignalTablesInterface_PyPlot.jl),
GLMakie (interactive plots in an OpenGL window; via SignalTablesInterface_GLMakie.jl),
WGLMakie (interactive plots in a browser window; via SignalTablesInterface_WGLMakie.jl),
CairoMakie (static plots on file with publication quality; via SignalTablesInterface_CairoMakie.jl).
Furthermore, there is a dummy implementation included in SignalTables.jl that is useful when performing tests with runtests.jl, in order that no plot package needs to be loaded during the tests:
- SilentNoPlot (= all plot calls are silently ignored).
Installation
julia> ]add SignalTables
add SignalTablesInterface_PyPlot # if plotting with PyPlot desired
# once registration processs finished
add SignalTablesInterface_GLMakie # if plotting with GLMakie desired
add SignalTablesInterface_WGLMakie # if plotting with WGLMakie desired
add SignalTablesInterface_CairoMakie # if plotting with CairoMakie desiredIf you have trouble installing SignalTablesInterface_PyPlot, see Installation of PyPlot.jl
Installation of PyPlot.jl
SignalTablesInterface_PyPlot.jl uses PyPlot.jl which in turn uses Python. Therefore a Python installation is needed. Installation might give problems in some cases. Here are some hints what to do (you may also consult the documentation of PyPlot.jl).
Before installing SignalTablesInterface_PyPlot.jl make sure that PyPlot.jl is working:
]add PyPlot
using PyPlot
t = [0,1,2,3,4]
plot(t,2*t)If the commands above give a plot window. Everything is fine.
If you get errors or no plot window appears or Julia crashes, try to first install a standard Python installation from Julia:
# Start a new Julia session
ENV["PYTHON"] = "" # Let Julia install Python
]build PyCall
exit() # Exit Juila
# Start a new Julia session
]add PyPlot
using PyPlot
t = [0,1,2,3,4]
plot(t,2*t)If the above does not work, or you want to use another Python distribution, install a Python 3.x distribution that contains Matplotlib, set ENV["PYTHON"] = "<path-above-python-installation>/python.exe" and follow the steps above. Note, SignalTablesInterface_PyPlot is based on the Python 3.x version of Matplotlib where some keywords are different to the Python 2.x version.
Release Notes
Version 0.4.4
- Adapted to GLMakie 0.8 (
textsizereplaced byfontsizein src/makie.jl)
Version 0.4.3
- Minor improvements when printing a SignalTable.
Version 0.4.2
- Fix issue #6: signalTableToDataFrame(..) is now working if the first signal is not a Var(..).
- Minor improvement in JSON generation.
Version 0.4.1
getSignalNames(signalTable; getVar=true, getPar=true, getMap=true): New keyword arguments getVar, getPar, getMap to only return names of the specified signal categories.
writeSignalTable(...): Some issues corrected.
@error replaced by error(..).
Version 0.4.0
- New signal-type Map added (additionally to Var und Par signals) with two new functions Map(..), isMap(..).
- Output of showInfo(..) improved.
- Non-backwards compatible changes: Function showInfo(..) has optional keywords arguments showVar, showPar, showMap, showAttributes, instead of the previous Var, Par, attributes.
Version 0.3.5
- @usingPlotPackage(): If SilentNoPlot selected, use "using SignalTables.SilentNoPlot" instead of "import SignalTables.SilentNoPlot: plot ..:".
- writeSignalTable(..): Arrays get an additional key
layout = "column-major"to clearly define that storage is in column-major order. Furthermore, if a signal has an alias key, then the values or value array is not stored on file.
Bug fixes
- writeSignalTable(..): If arrays or numbers have Unitful units, these units are stripped off and provided via key
unitas a string.
Version 0.3.4
- Bug fix in usePreviousPlotPackage()
Version 0.3.3
- Bug fix: getValuesWithUnit(..) is now correctly returning the values vector, if no unit is defined.
Version 0.3.2
- Add makie.jl to be used by Makie backends.
- For backwards compatibilty to ModiaResult, also accept ENV["MODIAPLOTPACKAGE"] instead of ENV["SignalTablesPlotPackage"] to define plot package - at all places (some parts have been missing).
Version 0.3.1
- writeSignalTable(..): Do not store elements, that cannot be mapped to JSON + add _classVersion to signal table on file.
- For backwards compatibilty to ModiaResult, also accept ENV["MODIAPLOTPACKAGE"] instead of ENV["SignalTablesPlotPackage"] to define plot package.
Version 0.3.0
- Slightly non-backwards compatible to 0.2.0.
- Various new functions (e.g. storing a signal table in JSON format on file).
- DataFrames.jl, Tables.jl are supported as signal tables.
- Plotting/flattening: Support of Measurements.jl and MonteCarloMeasurements.jl
- Docu improved.
- Bug with PlotPackage "SilentNoPlot" fixed.
SignalTables/test/runtests.jlruns the tests with plot package "SilentNoPlot" (instead of the activated plot package).- New file
SignalTables/test/runtests_with_plot.jlruns the tests with the activated plot package.
Version 0.2.0
Version, based on ModiaResult.jl. Changes with respect to ModiaResult.jl:
Underlying data format made much simpler, more general and more useful:
- Dictionary of multi-dimensional arrays as function of one or more independent variables with potentially missing values.
- Also parameters can be stored in the dictionary and are supported, e.g., for plotting.
- Variables and parameters are dictionaries that store the actual values (e.g. arrays), and additional attributes.
- Values are stored without units and the units are provided via the additional string attribute
:unit. A unit can be either hold for all elements of an array, or an array of units can be provided defining the units for all variable elements. - A new function to flatten and convert a signal array for use in plots or traditional tables.
- Since signals are arrays, all the Julia array operations can be directly used, e.g. for post-processing of simulation results.
- write/save on JSON and JDL (HDF5) files.
Furthermore
- Documentation considerably improved and made more user-oriented.
- The Abstract Interfaces defined more clearly.
- Several annoying bugs of ModiaResult.jl are no longer present.
Version 0.1.0
Initial version used for registration.
Main developer
Martin Otter, DLR - Institute of System Dynamics and Control